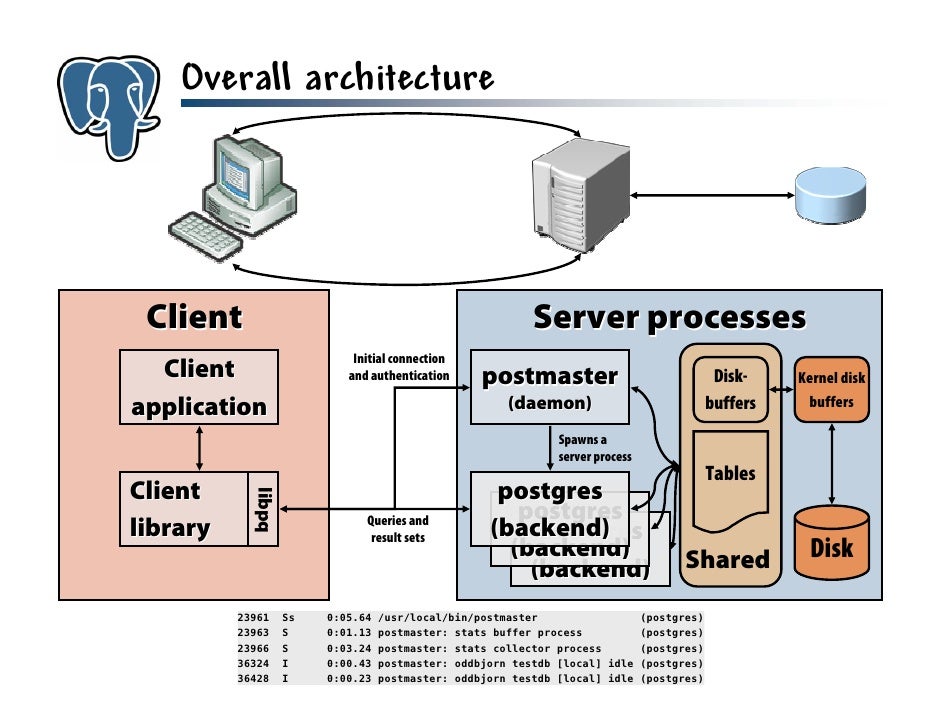
Databases
Now we'll be seeing a complete system for storing data on the disk.
No more reading in a file in order to edit it. No more managing which key is unique- name, id, etc.
The down side is that we are introducing another self-contained complex system.
In order to interact with this system we will need to communicate with it over the network, and send it commands in a special language- SQL.
We will be starting out working with just the database itself, and then we will integrate it into our app.
Objectives
- Understand the added compexity of the DB system
- Connect to a PostgreSQL database using
psql - Use SQL to create a database and tables
- Use SQL to insert, select, update, and delete data
- Understand what Primary Keys are
What is a database?
- It is a program that enforces structure on your data and allows a computer to quickly retreive data.
- A database should support CRUD operations
Why Use a Database?
- Data is structured
- Databases are transactional
- Data retrevial is fast
- Has a system for remote access
- Has a system for backup
Types of Databases
RDBMS (Relational Database Management System) The most common type of database today is a relational database. Relational databases have tabular data with rows for each instance of data and columns for each attribut of that data. Tables may refer to one another. Relational databases typically use SQL (Structured Query Language).
Brands of Relational Databases
- Postgres
- MySQL
- Oracle (Commercial Product with lots of features)
- Sybase
- Microsoft SQL Server
- SQLite (Good for mobile development/very small applications)
Cloud Storage This is a very vague term and can be used to mean lots of things. Typically it is a system in which your data is stored and managed by a company so you don't have to worry about losing it. Examples included AWS (Amazon Web Services), Rackspace, MS Azure
NoSQL There is also a school of thought called NoSql. It is often a Key Value storage system and is not relational. This is typically used in applications where a database does not scale well. Example technologies include MongoDB, Apache CouchDB, SimpleDB.
How are databases used in the wild?
Every app needs to store data. The most popular data store by a wide margin is still something that runs SQL queries. These come in many different forms, but postgres is the DB we will be using in Rails and has been gaining popularity over mySql (it's main open source sql competitor) for the last 5 years. Other non-open source database systems include: Oracle, Microsoft SQL Server, Sybase, etc.