Relational Tables in SQL - Many to Many
Many-to-many with join tables
The only way to store the data needed in a many-to-many relationship is to add a join table. These tables allow records to be created that reference both tables at once. They are really meant to only hold foreign keys.
Joins
The join statement fuses the results of queries in two tables together.
If it seems like the information is incomplete, we can add more join clauses to get a complete dataset, but in practice this will mostly be done in the javascript/ruby side.
There are four kinds of joins, but for join tables we will only be using inner joins.
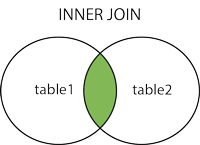
SELECT table1.column1,table1.column2,table2.column1,....
FROM table1
INNER JOIN table2
ON table1.matching_column = table2.matching_column;
table1: First table.
table2: Second table
matching_column: Column common to both the tables.
SELECT owners.name, dogs.name
FROM dogs
INNER JOIN owners
ON (owners.id = dogs.owner_id);
SELECT owners.name, dogs.name
FROM dogs
INNER JOIN owners
ON (owners.id = dogs.owner_id)
WHERE owner.id = 1;
Many-to-many: Shops and Products
A shop has many products and products can be in many stores.
tables.sql:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS shops (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS products (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS shop_products (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
product_id INTEGER,
shop_id INTEGER
);
Create Shops
INSERT INTO shops (name) VALUES ('Alex''s Boutique');
INSERT INTO shops (name) VALUES ('Nick''s Bargains');
INSERT INTO shops (name) VALUES ('Worst Buy');
Create Products
INSERT INTO products (name) VALUES ('Baby Powder');
INSERT INTO products (name) VALUES ('Boxing Gloves');
INSERT INTO products (name) VALUES ('Hulk iPhone Case');
INSERT INTO products (name) VALUES ('Oversize Novelty Toothbrush');
Fill join table
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (1,2);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (1,3);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (2,3);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (2,1);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (3,3);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (4,3);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (4,2);
INSERT INTO shop_products (product_id, shop_id) VALUES (4,1);
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Alex's Boutique |
| 2 | Nick's Bargains |
| 3 | Worst Buy |
| id | name |
|---|---|
| 1 | Baby Powder |
| 2 | Boxing Gloves |
| 3 | Hulk iPhone Case |
| 4 | Oversize Novelty Toothbrush |
| product | shop |
|---|---|
| Baby Powder (1) | Nick's Bargains (2) |
| Baby Powder (1) | Worst Buy (3) |
| Boxing Gloves (2) | Worst Buy (3) |
| Boxing Gloves (2) | Alex's Boutique (1) |
| Hulk iPhone Case (3) | Worst Buy (3) |
| Oversize Novelty Toothbrush (4) | Alex's Boutique (1) |
| Oversize Novelty Toothbrush (4) | Nick's Bargains (2) |
| Oversize Novelty Toothbrush (4) | Worst Buy (3) |
Queries:
Get every product in Nick's Bargains (id = 2)
SELECT shop_products.shop_id, products.name
FROM products
INNER JOIN shop_products
ON (shop_products.product_id = products.id)
WHERE shop_products.shop_id = 2;
Get every shop that carries oversize novelty toothbrushes (id = 4)
SELECT shop_products.product_id, shops.name
FROM shops
INNER JOIN shop_products
ON (shop_products.shop_id = shops.id)
WHERE shop_products.product_id = 4;
Many-to-many: Twitter Followers
You have many followers on twitter AND you follow many people.
tables.sql:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name TEXT,
);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS followers (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
user_id INTEGER,
follower_user_id INTEGER
);
Create Users
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('brad');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('sarah');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('donald');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('fred');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('ray');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('nick');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('akira');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('albert');
INSERT INTO users (name) VALUES ('charles');
Users follow each other
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (1,2);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (1,3);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (1,4);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (5,1);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (6,2);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (6,5);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (8,5);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (7,5);
INSERT INTO followers (user_id, follower_user_id) VALUES (9,5);
Get your followers:
SELECT followers.follower_user_id
FROM users
INNER JOIN followers
ON (followers.user_id = users.id)
WHERE users.id = 1;
Get people you're following:
SELECT users.id, users.name
FROM users INNER JOIN followers
ON (followers.user_id = users.id)
WHERE followers.follower_user_id = 1;
Pairing Exercise
Run the above code.
further
Create a set of tables for dogs and owners. Owners have many dogs, and dogs have many owners.